Blinds
Blinds can be added to internal or external windows, glass doors, and skylight constructions. Blinds specify the properties of a window blind consisting of flat, equally-spaced slats. Unlike window shades, which are modeled as perfect diffusers, window blinds have solar and visible transmission and reflection properties that strongly depend on slat angle and angle of incidence of solar radiation.
Blinds can be located on the inside of the window (“interior blinds”), on the outside of the window (“exterior blinds”), or between two layers of glass (“between glass blinds”). When in place, the blind is assumed to cover all of the glazed part of the window, including dividers; it does not cover any of the window frame, if present. The plane of the blind is assumed to be parallel to the glazing. When the blind is retracted it is assumed to cover none of the window. The solar and thermal effects of the blind’s support strings, tapes, or rods are ignored. Slat curvature, if present, is ignored.
Blinds properties
Type
The choices are horizontal and vertical. “Horizontal” means the slats are parallel to the bottom of the window; this is the same as saying that the slats are parallel to the X-axis of the window. “Vertical” means the slats are parallel to Y-axis of the window.
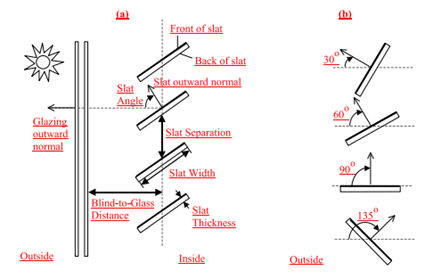
The figure below shows a graphic representation of blind properties.
Slat width
This is the width of the slat measured from edge to edge.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x <= 1000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
3 to 30 mm; 0.01 to 1.5 in
|
|
Units:
|
mm; in
|
Slat separation
This is the distance between the front of a slat and the back of the adjacent slat.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x <= 1000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
3 to 30 mm; 0.01 to 1.5 in
|
|
Units:
|
mm; in
|
Slat thickness
This is the distance between the faces of a slat.
|
Default value:
|
0.0006 mm; 0.00025 in
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 < x <= 1000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
3 to 30 mm; 0.01 to 1.5 in
|
|
Units:
|
mm; in
|
Slat angle
This is the angle (degrees) between the glazing outward normal and the slat outward normal, where the outward normal points away from the front face of the slat (degrees).
|
Default value:
|
45 degrees
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x <= 180
|
|
Typical Range:
|
30 to 60
|
|
Units:
|
degrees
|
Slat conductivity
This is the thermal conductivity for the slat.
|
Default value:
|
221 W/mK
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x <= 100,000
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
W/mK; Btu/hr•ft•°F
|
Slat beam solar transmittance
This is the beam solar transmittance of the slat. It is assumed to be independent of the angle of incidence on the slat. Any transmitted beam radiation is assumed to be 100% diffuse (i.e., slats are translucent).
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Outside slat beam solar reflectance
This is the beam solar reflectance of the outside (front) side of the slat. It is assumed to be independent of the angle of incidence (matte finish). This means that slats with a large specularly-reflective component (shiny slats) are not well modeled.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Inside slat beam solar reflectance
This is the beam solar reflectance of the inside (back) side of the slat. It is assumed to be independent of the angle of incidence (matte finish). This means that slats with a large specularly-reflective component (shiny slats) are not well modeled.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Slat beam visible transmittance
This is the beam visible transmittance of the slat. It is assumed to be independent of angle of incidence on the slat. Any transmitted visible radiation is assumed to be 100% diffuse (i.e., slats are translucent).
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Outside slat beam visible reflectance
This is the beam visible reflectance on the outside (front) side of the slat. It is assumed to be independent of angle of incidence (matte finish). This means that slats with a large specularly-reflective component (shiny slats) are not well modeled.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Inside slat beam visible reflectance
This is the beam visible reflectance on the inside (back) side of the slat. It is assumed to be independent of angle of incidence (matte finish). This means that slats with a large specularly-reflective component (shiny slats) are not well modeled.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Infrared hemispherical transmittance
This is the slat Infrared transmittance. It is zero for solid metallic, wooden or glass slats, but may be non-zero in some cases (e.g., thin plastic slats).
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x < 1
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
N/A
|
Minimum closing angle
This is the minimum allowed slat angle in degrees. It is only used the shading control for the window varies with the slat angle. See Window constructions for more information.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x <= 180
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
degrees
|
Maximum opening angle
This is the maximum allowed slat angle in degrees. It is only used the shading control for the window varies with the slat angle. See Window constructions for more information.
|
Default value:
|
blank
|
|
Min & Max:
|
0 <= x <= 180
|
|
Typical Range:
|
N/A
|
|
Units:
|
degrees
|