Curve tab
There are two sets of curves for Water Cooled Chillers depending on the operating mode of the chiller: Cooling Mode and Ice Storage. The description of the curves are below. The Water Cooled–Simple chiller uses Entering Condenser Temperature in the curves while the Water Cooled–Detailed chiller uses Leaving Condenser Temperature in the curves.
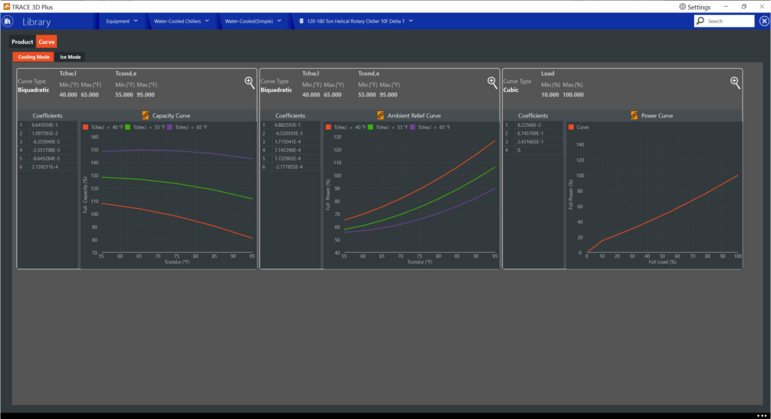
Cooling Mode
Capacity Curve
This biquadratic curve shows the percentage of full cooling capacity as a function of the condenser fluid temperature and the leaving chilled water temperature. Inputs consists of two independent variables, six coefficients, and min and max values for each of the independent variables. The equation for the capacity curve is:
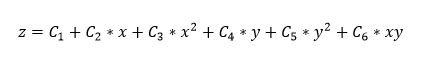
Where:
Z = Cooling Capacity
C1 to C6 = coefficients
X = Condenser temperature
Y = Chilled Water Temperature
The curve has the following fields:
|
X Axis:
|
Condenser fluid temperature (°F, °C). Depending on the input for Condenser Temperature Type on the product’s tab, this axis will be either the Leaving or Entering Condenser Fluid temperature.
|
|
Y Axis:
|
Cooling Capacity (%).
|
|
Tchw,l Min / Max :
|
Minimum and maximum temperature values (°F, °C) for the Chilled water leaving temperature variable. These values determine the three chilled water temperatures plotted, one is the maximum, one is the minimum and the last one is the midpoint between them.
|
|
Tcond,e Min / Max or Tcond,l Min / Max :
|
Minimum and Maximum temperature values (°F, °C) for the Condenser Temperature variable on the X axis. E is for entering, l is for leaving condenser water temperature. The Water Cooled–Simple chiller uses Entering Condenser Temperature in the curves while the Water Cooled–Detailed chiller uses Leaving Condenser Temperature in the curves.
|
Ambient Relief Curve
This biquadratic curve represents the chiller’s energy input to cooling output ratio as a function of the condenser fluid temperature and the leaving chilled water temperature.
Inputs consists of two independent variables, six coefficients, and min and max values for each of the independent variables. The equation for the capacity curve is:
Where:
Z = Chiller’s electric consumption (%)
C1 to C6 = coefficients
X = Condenser temperature
Y = Leaving Chilled Water Temperature
The curve has the following fields:
|
X Axis:
|
Condenser fluid temperature (°F, °C). Depending on the input for Condenser Temperature Type on the product’s tab, this axis will be either the Leaving or Entering Condenser Fluid temperature.
|
|
Y Axis:
|
Chiller's electric consumption (%).
|
|
Tchw,l Min / Max :
|
Minimum and maximum temperature values (°F, °C) for the Chilled water leaving temperature variable. These values determine the three chilled water temperatures plotted, one is the maximum, one is the minimum and the last one is the midpoint between them.
|
|
Tcond,e Min/Max; Tcond, l Min / Max:
|
Minimum and Maximum temperature values (°F, °C) for the Condenser Temperature variable on the X axis. E is for entering, L is for leaving condenser water temperature. The Water Cooled–Simple chiller uses Entering Condenser Temperature in the curves while the Water Cooled–Detailed chiller uses Leaving Condenser Temperature in the curves.
|
Power Curve (simplified Chillers)
This quadratic curve represents the chiller’s electric consumption at part load with operating temperatures at design values. This curve is generated by plotting the percentage of full load power consumed by the compressor vs. the percentage of full load cooling capacity. The curve output should be 0% power when there is 0% load and should be 100% power when there is 100% load.
The equation for the Power Curve is:
Where:
y = Chiller’s electric consumption (%)
C1 to C3 = coefficients
X = Part Load
The curve has the following fields:
|
X Axis:
|
Full Load (%)
|
|
Y Axis:
|
Full Power (%).
|
|
Capacity Min/Max:
|
The curve can be selected as quadratic or cubic.
|
|
Load Min/Max
|
Minimum and Maximum Load Percentage
|
Power Curve (detailed Chillers)
This bicubic curve represents the chiller’s electric consumption at part load with operating temperatures at design values. This curve is generated by plotting the percentage of full load power consumed by the compressor vs. the percentage of full load cooling capacity. The curve output should be 0% power when there is 0% load and should be 100% power when there is 100% load.
The equation for the Power Curve is:
Where:
z = Chiller’s electric consumption (%)
C1 to C6 = coefficients
x = Condenser Temperature
y = Part Load Ratio
The curve has the following fields:
|
X Axis:
|
Full Load (%)
|
|
Y Axis:
|
Full Power (%).
|
|
Capacity Min/Max:
|
The curve can be selected as quadratic or cubic.
|
|
Load Min/Max
|
Minimum and Maximum Load Percentage
|