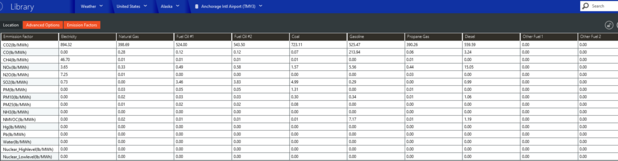
Emission Factors
The Emission Factors tab allows you to enter the Emission Factors per fuel type in order to measure the Environmental Impact released to the atmosphere per contaminant while creating each type of utility.
This is found in the 3rd tab of the Standard Weather files for United States locations only. Non-US weather file locations show zeros for all emissions. Local data can be entered into a copy of these weather files for use with the Carbon Footprint report.

There are ten allowable utility types: Electricity, Natural Gas, Fuel Oil #1, Fuel Oil #2, Coal, Gasoline, Propane, Diesel, Other Fuel #1 and Other Fuel #2.
Emissions data in a weather file can be edited by making a copy of the original library member and editing the values within the copied file. Trace Standard Library members cannot be directly edited.
Below is the list of the references for all Emissions Factors found in the US location files.
Version 7.00.214 and earlier
Electricity Emission factors for every state in the United States are populated from the Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database (eGRID) 9th edition Version 1.0 State File (Year 2010 Data) ST10 tab.
The following Columns of Values have been imported into the US domestic locations.
Column Q: NOx total output emissions rate, STNOXRTA
Column S: SO2 total output emissions rate, STSO2RTA
Column T: CO2 total output emissions rate, STCO2RTA
Column U: CH4 total output emissions rate, STCH4RTA
Column V: N2O total output emissions rate, STN2ORTA
Emissions from all other fuel types are identical for all U.S domestic locations. This data is not state specific but has a single value by fuel type and chemistry for all US locations.
The following data sources was used for all non-electric generated energy.
Natural Gas:
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement D, July 1998
Chapter 1 External Combustion Sources,
Section 1.4 Natural Gas Combustion
FuelOilNo1:
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement E,
Sept 1998
Chapter 1 External Combustion Sources
Section 1.3 Fuel Oil Combustion
FuelOilNo2:
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement E,
Sept 1998
Chapter 1 External Combustion Sources
Section 1.3 Fuel Oil Combustion
Coal: (Specifically Bituminous and Subbituminous Combustion)
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement E,
Sept 1998
Chapter 1 External Combustion Sources
Section 1.1 Bituminous and Subbituminous Coal Combustion
Diesel & Gasoline:
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement B, October 1996
Chapter 3 Stationary Internal Combustion Sources
Section 3.3 Gasoline and Diesel Industrial Engines
Propane: (Note: EnergyPlus does not include LPG as a fuel type use Propane as the resource name.)
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement B, October 1996
Chapter 1 External Combustion Sources
Section 1.5 Liquified Petroleum Gas Combustion
Two additional columns have been provided for use for Other Fuel 1 and Other Fuel 2, these can be used for FuelOil#4 or FuelOil#6 or other sources.
Data reference for FuelOil#4 and FuelOil#6 can be found from this source.
USEPA Compilation of Air Pollutant Emissions Factor, AP-42, Fifth Edition.
Volume 1: Stationary Point and Area Sources Supplement E,
Sept 1998
Chapter 1 External Combustion Sources
Section 1.3 Fuel Oil Combustion
There are ten allowable utility types: Electricity, Natural Gas, Fuel Oil #1, Fuel Oil #2, Coal, Gasoline, Propane, Diesel, Other Fuel #1 and Other Fuel #2.
The emission factors are:
-
NOx Emission Factor is the mass of nitrogen oxides released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
SO2 Emission Factor is the mass of sulfur dioxide released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
CO2 Emission Factor is the mass of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
CH4 Emission Factor is the mass of methane released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
N2O Emission Factor is the mass of nitrous oxide released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
CO Emission Factor is the mass of carbon monoxide released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
Hg Emission Factor is the mass of mercury released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
NH3 Emission Factor is the mass of ammonia released into the atmosphere for each utility type.NMVOC Emission Factor is the mass of non-methane volatile organic compounds (which include propane, butane, and ethane) released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
Pb Emission Factor is the mass of lead released into the atmosphere for each Fuel type.
-
M Emission Factor is the mass of particulate matter (including PM10 and PM2.5) released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
PM10 Emission Factor is the mass of particulate matter 10 (with an aerodynamic diameter of less than 10 microns) released into the atmosphere for each Fuel type.
-
PM2.5 Emission Factor is the mass of particulate matter 2.5 (2.5 microns in diameter or smaller) released into the atmosphere for each utility type.
-
Water Emission Factor is volume of water consumed or evaporated in the generation of each utility type.
-
Nuclear High Level Emission Factor is the mass of high-level nuclear waste, removed as spent nuclear fuel from a nuclear reactor once it no longer is efficient at powering the reactor. Once a year, approximately one-third of nuclear fuel is replaced with new fuel. This used fuel is called spent nuclear fuel and is highly radioactive; containing plutonium and other radionuclides.
-
Nuclear Low Level Emission Factor is the volume of low-level nuclear waste, removed from a nuclear reactor after radiation contamination.
|
Default: Default values for the other utility types are an example, real values per state should be entered
|
|
Min & Max: 0 to 100
|
|
Typical Range: N/A
|
|
Units: lb/MWh; g/MJ
|
Site to Source Energy Conversion Factors
These values are provided on the Simulation Settings – Energy Simulation Parameters tab. These values can be replaced by the program user to reflect their current local source energy providers.
This multiplier is used to convert the project’s on-site energy usage to the energy produced by the generation source(s) to supply the full year energy to the project. Separate columns in the Energy Report: Site Consumption Summary provide both the Site based energy usage and the total Source based energy usage.
The reference for the Electricity Site to Source conversion factor is provided by the EnergyPlus version 24.2.0 Input – Output Reference Manual Section 5.1.17.1.2. Table 5.8 is a compilation of multiple US EPA source data.
Section 5.2, Table 5.0.
For Coal the reference is the Bituminous Coal data value.
Document Identification: Technical Report, NREL/TP-550-38617, Revised 2007, Source Energy and Emissions Factors for Energy Use in Building, M. Deru and P. Torcellini
Global Warming Potential (GWP) of Methane, and Nitrous Oxide and Carbon Dioxide
These values are provided on the Simulation Settings – Energy Simulation Parameters tab.
These three chemicals have been identified by the IPCC Greenhouse Gas Protocol as having a larger impact on the environment than CO2. Therefore, they have a multiplier to convert their emissions data to CO2 equivalent emissions.
The reference for these values is the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The data provided for Trace 3Dplus comes from the Fourth Assessment Report (2007), AR4 for the GWP for the 100-year time horizon.
This reference is available here: Microsoft Word - Global-Warming-Potential-Values.docx